Guidelines
- Home
- Guidelines
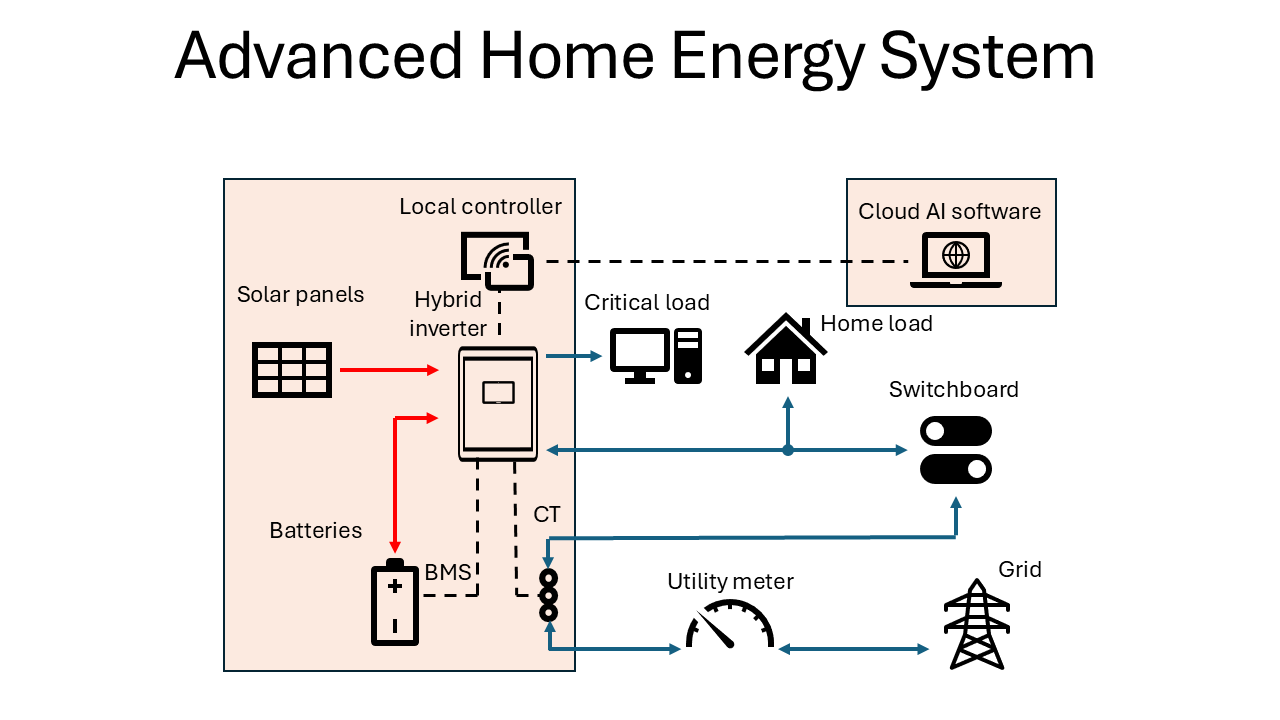
General overview of Advanced Home Energy System
The Advanced Home Energy System consists of four main components:
- Solar panels
- Hybrid inverter
- Battery set
- AI-based cloud software.
Usually, the functionality of the Advanced Home Energy System includes the following strategies.
- Peak shaving. Low consumption – buy and store, high consumption – consume from storage.
- Load shifting. High solar activity – store exceeded energy, no solar activity – consume from storage.
- Arbitrage. Low rate – buy from & store, high rate – sell to grid.
- Load management. Smart load regulation (EV charging, heat pumps, water boilers, etc).
Peak Shaving – how it works
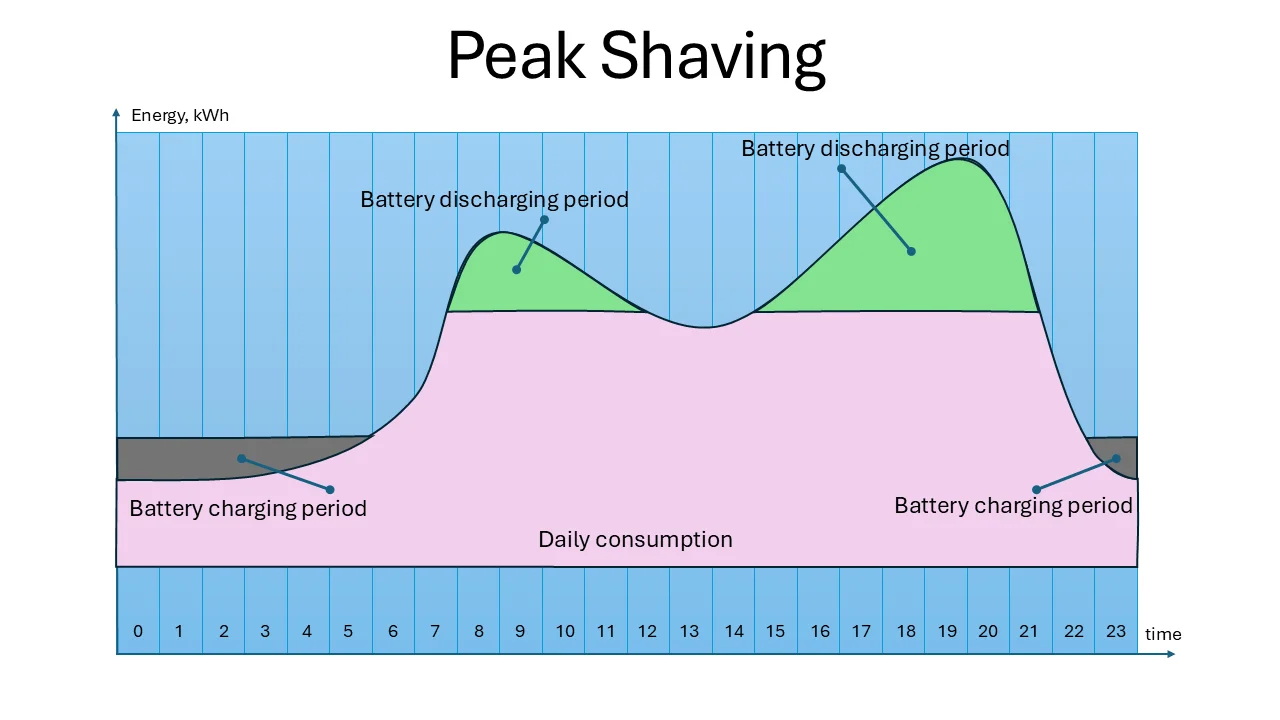
Peak Shaving is a powerful energy management strategy that helps reduce energy costs and provide power stability.
The Advanced Home Energy System is monitoring energy demand. It continuously tracks the household’s energy consumption and identify peak demand periods (when appliances, heating, and cooking are active).
The system decides to charge the battery during low-demand periods – typically at night or when energy prices are cheaper. Batteries are charging from the grid or solar panels. And vice versa, discharging during peak demand – detecting a surge in power usage, the battery discharges energy to meet this demand.
By supplying stored energy instead of drawing power from the grid, the system effectively reduces the home’s peak demand.
Example. Imagine a household that typically consumes 10 kW of power but occasionally spikes to 15 kW when cooking dinner or using a sauna. Instead of pulling the additional 5 kW from the grid at premium rates, the Advanced Home Energy System delivers extra energy.
Load Shifting – how it works
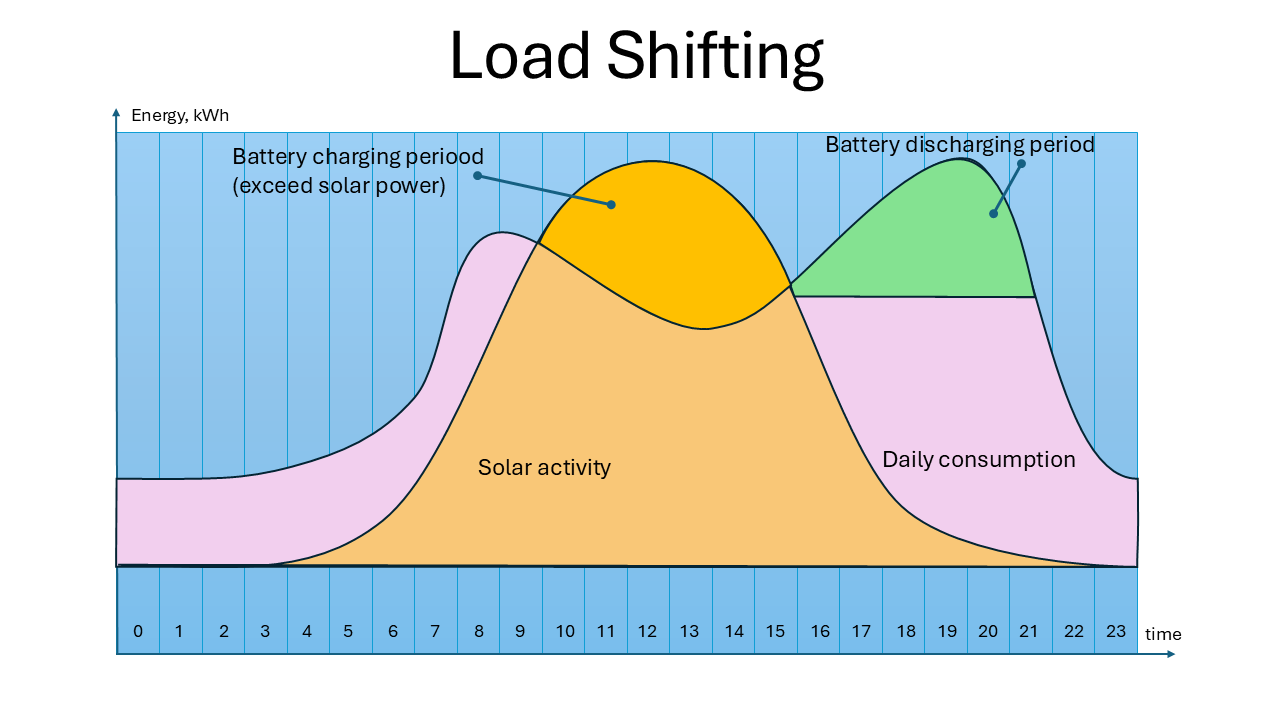
The Load Shifting strategy maximizes savings and effectiveness of solar generation. This is ideal for homes with solar panels.
The Advanced Home Energy System is monitoring the household’s demand and solar energy generation.
AI algorithms identify the most cost-effective times to charge and discharge the battery depending on the proportion of consumption-generation, weather forecast, behaviour patterns, and others.
Excess solar energy that’s not immediately consumed is stored in the battery instead of being exported to the grid. This ensures that self-generated energy is available later when solar production drops. When energy prices are higher (typically in the evening and night) or solar production is low, the battery discharges to power the home.
The system may also prioritize battery discharge during cloudy days or winter months when solar production is lower.
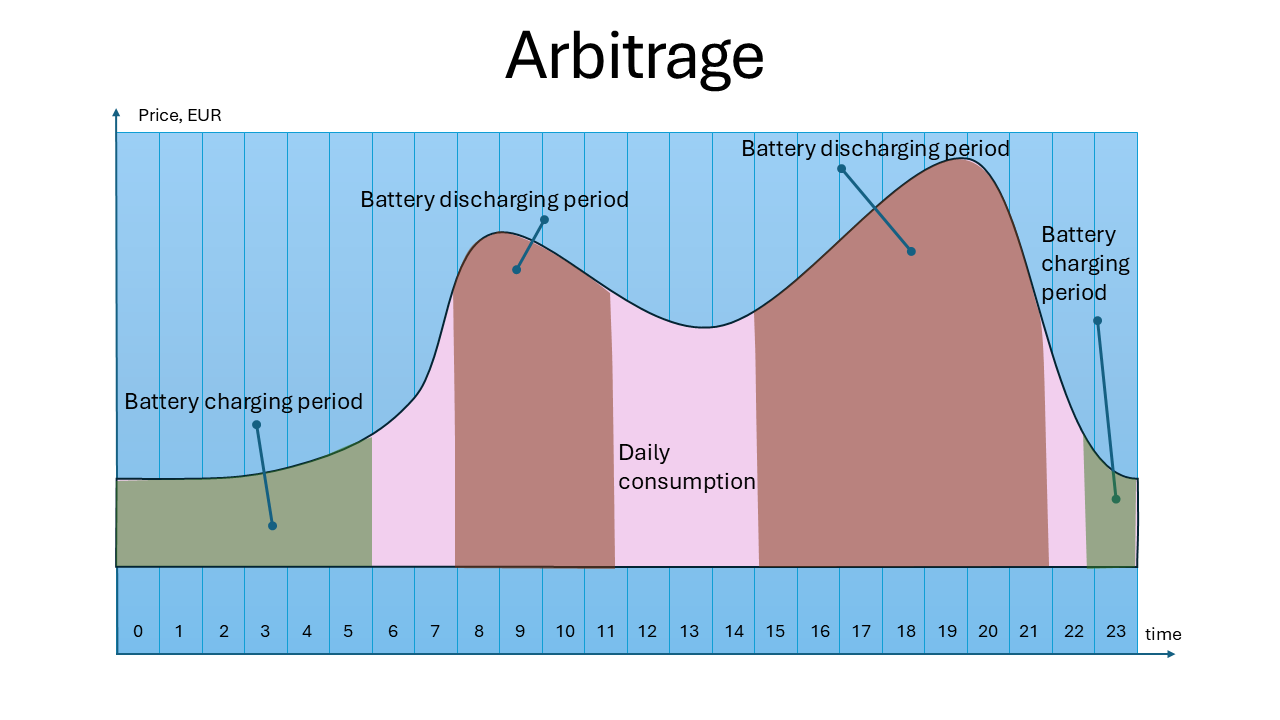
Arbitrage – how it works
The Arbitrage strategy has many commonalities with the Peak Shaving strategy. In case of Arbitrage, the homeowner makes an effort for the energy price, not for the energy consumption.
AI-based algorithms decide for themselves when the charging or discharging process is started and finished.
The main feature is financial benefits – saving costs or even getting income from energy consumption.
NB! It is possible to use Arbitrage with solar panels or without ones.
Load management – how it works
The Advanced Home Energy System intelligently allocates energy by shifting smart loads to off-peak hours or when solar production is high.
For example, the system may delay EV charging until overnight when energy demand is lower.
When household demand exceeds available solar power or low-cost grid energy, the battery discharges to cover the gap.
Load Management strategy usually includes control for the home devices:
- EV chargers
- Heat pumps
- Water boilers